|
MELATONIN
(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/melatonin)
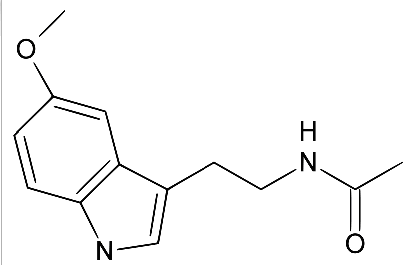
Melatonin is a hormone found in all
living creatures, produced by pinealocytes in the
pineal gland (located in the brain).
It was discovered by Lerner in 1958.
Normally, the production of melatonin by
the pineal gland is inhibited by light and permitted by
darkness. For this reason melatonin has been called "the
hormone of darkness." The secretion of melatonin peaks
in the middle of the night, and gradually falls during
the second half of the night.
Some studies are not considering
melatonin as a hormone because it is produced by
different organs during the day, and because dose of
some mg per day do not cause side effects (such as other
hormones).
Melatonin is practically nontoxic and
exhibits almost no short-term side effects. However,
melatonin derived from animal sources may be
contaminated with viral material; synthetic melatonin
may be taken to avoid this risk. No studies have been
conducted yet to determine whether there are any
long-term side effects.
Even though it is seen as a relatively
safe, benign drug, especially to herbal enthusiasts, it
can cause some unwanted side effects, especially at high
doses. But it is sold in supermarkets and herbalist's
shop, without medical prescription. Some people think it
is a nourishment, not a medicine, but you can have some
side effects, except you doctor suggest about dose and
time of consumption.
First use of melatonin as therapy was on
1969 with the trials of dr. Luigi Di Bella that guessed
a potential therapy (it is a current debate about use of
melatonin in his treatments).
Dosages are designed to raise melatonin
levels for several hours to enhance quality of sleep,
but some studies suggest that smaller doses are just as
effective at improving sleep quality, and it appears to
have some use against circadian rhythm sleep disorders,
such as jet lag. It seems melatonin synchronizes
biological clock. A recent issue of British Medical
Journal has considered 10 random trials where melatonin
has been compared with placebo in long distances
travelers. 8 of them shown melatonin effective in
jet-lag effects.
2 to 5 mg of melatonin is enough before
sleeping the day after the flight and in the next 2/4
days, to settle the rate on the new time zone.
The issue confirms that the melatonin is
not registered as a pharmacy in the EU.
This is because of the law on patents (EU
countries, also in Italy) where natural substances are
not patentable.
The prescription is not forbidden, but
deprives the market of this product and makes its
finding hard.
1
2 |